
 Global Hotline
Global Hotline
Complete Analysis of LCD Display Module Structure and Mold Costs: From Liquid Crystal Glass to Complete Backlight
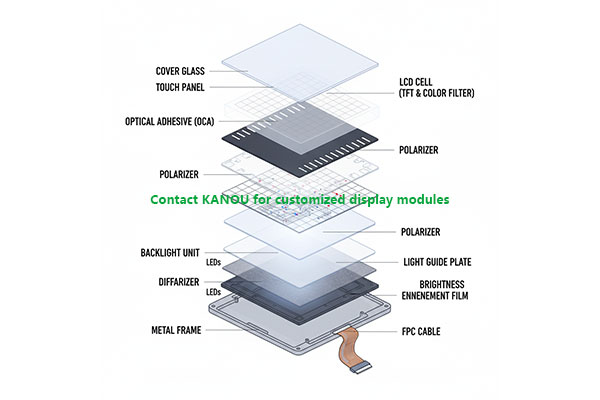
An LCD display module can be clearly divided into two core systems: the display system and the backlight system. For customization, understanding the mold cost for each component is key. Below, we use a 10.1-inch display as an example to analyze the function of each component one by one, along with an approximate estimate of the mold costs.
This part is responsible for receiving signals and generating images.
1. Liquid Crystal Glass
Description: This is the "heart" of the display, the core technology. It consists of two parallel glass substrates filled with liquid crystal material. By applying different voltages, the alignment state of the liquid crystal molecules is changed, thereby controlling the light transmittance of each pixel.
Key Terms: TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) array, CF (Color Filter), which are located on the upper and lower substrates respectively, working together to produce color images.
Mold Cost: Fully customizing liquid crystal glass (e.g., special resolution, pixel arrangement) does not involve traditional molds but requires high photomask costs, typically ranging from $15,000 to $150,000 USD, with a very long cycle time. Therefore, customization is usually based on cutting and driving design of existing glass substrates.
2. Polarizer
Description: There are two pieces, attached to the upper and lower surfaces of the liquid crystal glass. Their function is similar to a "fence," filtering natural light into linearly polarized light in a single direction. After modulation by the liquid crystal molecules, the combination of the upper and lower polarizers ultimately presents an image with varying brightness and darkness.
Customization Points: Can be customized according to requirements for different transmittance, thickness, or special functions (such as anti-glare, AG/AR treatment).
Mold Cost: Polarizers themselves are supplied in rolls. Customization mainly involves cutting and functional treatment, which usually does not incur high mold costs, or may only require a cutting die costing a few hundred dollars.

3. FPC
Description: Flexible Printed Circuit board. It is the "bridge" connecting the liquid crystal glass to the external main control driver board. One end of the FPC is bonded to the ITO lines of the liquid crystal glass via ACF (Anisotropic Conductive Film) under heat and pressure, while the other end connects to the mainboard via a connector.
Customization Points: The length, width, bending direction, pin definition, and connector type of the FPC can all be customized, making it a key component for adapting to product structural design.
Mold Cost: If the pin definition, shape, or number of layers requires complete customization, the FPC needs molds (for circuit patterns, coverlay, etc.). The mold cost for a 10.1-inch specification is approximately $1,500 - $3,500 USD.
Part 2: Backlight System – Providing Uniform Light Source
LCD itself does not emit light; it requires a backlight system to provide uniform, bright illumination.
1. Light Source & Adapter PCB
Description: Typically uses edge-lit LED light bars. LED chips are soldered onto a narrow adapter PCB, which is then connected to the main FPC or backlight drive circuit via connectors or solder points. This is the light source starting point for the backlight.
Mold Cost: The adapter PCB is a rigid board. If customization is needed, the mold cost is relatively low, typically around $150 - $750 USD.
2. Light Guide Plate
Description: Usually made of highly transparent acrylic (PMMA). Its function is to evenly diffuse the point or line light source emitted by the side-mounted LEDs into a surface light source across the entire plate through dot pattern design and the principle of total internal reflection.
Customization Points: Size, thickness, and dot pattern design are key to the optical effect and require mold customization.
Mold Cost: The injection molding/cutting mold cost for a 10.1-inch light guide plate is approximately $2,800 - $5,600 USD, with laser dot design being the core cost.
3. Optical Films
Description: A set of multi-layer films stacked above the light guide plate to collectively optimize light. Usually includes a lower diffusion film, brightness enhancement films (typically two layers), and an upper diffusion film, which respectively serve to homogenize light, enhance brightness, and further blur the dot patterns.
Mold Cost: Optical films themselves are standard roll materials. Customization requires precision cutting dies, costing approximately $700 - $1,400 USD.
4. Plastic Frame
Description: Usually made of plastic material (such as PC, PS), formed by injection molding. Its function is to secure and carry all backlight components (films, light guide plate) and the liquid crystal glass, providing structural support.
Customization Points: Requires mold opening. Its structural design directly determines the overall thickness, strength, and fitting precision of the components.
Mold Cost: As a core structural component, the plastic injection mold cost for a 10.1-inch plastic frame is relatively high, approximately $5,000 - $10,000 USD, depending on complexity.

5. Upper Iron Frame
Description: A metal stamping part that wraps around the top edge of the plastic frame and liquid crystal glass. Its main functions are to clamp all components tightly together, ensuring structural stability, and providing electromagnetic shielding (EMI) and aesthetic appeal.
Customization Points: Requires mold opening (stamping mold). Its shape determines the width of the display's "black border" and is an important part of the appearance design.
Mold Cost: The stamping mold cost is approximately $2,000 - $4,000 USD.
6. Lower Iron Frame
Description: A metal stamping part located at the very bottom of the entire module. Its main role is to provide sturdy mechanical support, protect internal fragile components, and it usually features mounting holes for fixing the entire module into the customer's product.
Customization Points: Requires mold opening (stamping mold). Material, thickness, bending angles, and mounting structure are key.
Mold Cost: The stamping mold cost for a 10.1-inch lower iron frame is approximately $2,000 - $4,000 USD.
We hope this structural breakdown integrated with cost analysis provides you with more practical reference for evaluating your customization project. KANOU is ready to provide precise solutions and quotations based on your specific needs.
If you have preliminary structural sketches or size requirements, KANOU ← can immediately evaluate them and provide more targeted solutions and quotations.